Nutanix Disaster Recovery: Modern Policy-Driven Protection

Overview
Nutanix offers two distinct approaches to disaster recovery: Protection Domains (the battle-tested foundation) and Nutanix DR (the policy-driven evolution). This post explores both methods, their capabilities, when to use each approach, and how they complement each other. Understanding the difference is crucial for building DR strategies that match your operational model and scale requirements.
Disaster Recovery in 2025 Series - Part 3 This post continues our comprehensive disaster recovery series. New to the series? Start with the Complete Guide Overview to see the full roadmap. Catch up on Part 1 - Why DR Matters and Part 2 - Modern Disaster Recovery before diving in.
So far in this series I've covered why disaster recovery has become absolutely critical in 2025, and explored how modern DR platforms are delivering simplicity and automation that makes traditional approaches look primitive. Now it's time to get practical, and start diving into some details.
The Two Faces of Nutanix DR Protection
When people talk about "Nutanix DR", potentially they're actually referring to two distinctly different approaches that can serve different use cases and operational models. One represents the foundation that's been battle-tested for years, and the other represents the policy-driven future that's transforming how we think about business continuity.Understanding the difference is crucial for choosing the right solution for your environment.
The "Legacy" Approach - Protection Domains (Still Relevant)
Protection Domains represent the original Nutanix approach to data protection, managed through Prism Element (PE) and deeply integrated into AOS. Think of Protection Domains as the "classic" method, battle-tested in production environments for years and continues to serve specific use cases exceptionally well.
Key characteristics of Protection Domains:
- VM-centric management - You select specific VMs to protect and organize them into consistency groups
- Prism Element configuration - Managed at the cluster level through PE
- Manual orchestration - Recovery requires manual intervention and validation
- Snapshot-based - Leverages AOS native snapshot capabilities with efficient storage utilization
- Direct replication - Site-to-site replication without complex orchestration layers
When Protection Domains make sense:
- Simple, straightforward backup and replication requirements
- Small to medium environments where manual recovery is acceptable
- Scenarios where you need granular control over specific VMs
- Organizations that prefer cluster-level management over centralized policies
- Situations where the overhead of Prism Central isn't justified
The Modern Evolution - Nutanix Disaster Recovery (The Future)
Nutanix Disaster Recovery (often called "Leap" in earlier versions) represents the policy-driven, automation-first approach managed through Prism Central (PC). This is where Nutanix has invested heavily in recent years, and it shows in the sophisticated capabilities it delivers.
Key characteristics of Nutanix DR:
- Category-based management - Protection policies apply to categories, not individual VMs
- Prism Central orchestration - Centralized management across multiple clusters and cloud environments
- Automated recovery plans - Sophisticated boot sequencing, network mapping, and validation
- Policy-driven approach - Set the rules once, let the system handle the complexity
- Hybrid cloud native - Seamless integration with NC2 and public cloud environments
When Nutanix DR excels:
- Large-scale environments requiring consistent DR policies
- Hybrid cloud deployments spanning on-premises and public cloud
- Organizations needing automated failover capabilities
- Environments where compliance requires documented, tested recovery procedures
- Scenarios demanding sophisticated recovery orchestration and runbook automation
Understanding Protection Domains - The Foundation
Before diving into the modern approach, let's establish a solid understanding of Protection Domains since they form the conceptual foundation for everything that followed.
Core Protection Domain Constructs
Protection Domain (PD) - A logical grouping of VMs and/or files that need to be protected together. Think of this as your "unit of protection" - everything in a PD gets snapshotted and replicated on the same schedule with consistent restore points.
Consistency Group (CG) - A subset within a Protection Domain that ensures crash-consistent snapshots. This is critical for multi-VM applications where you need all components to be captured at exactly the same point in time (like an app server and its database).
Snapshot Schedule - Defines when snapshots are taken and how often they're replicated to remote sites. Your snapshot frequency should align with your RPO requirements - if you can tolerate losing 1 hour of data, snapshot every hour.
Retention Policy - Determines how many snapshots to keep locally and remotely. This balances storage costs against how far back you need to be able to restore.
Remote Site - The target Nutanix cluster for replication, which could be another on-premises cluster, a cloud-based NC2 deployment, or even a storage-only node for backup purposes.
Protection Domain Workflow
The traditional Protection Domain workflow follows a straightforward pattern:
- Create Protection Domain - Define the logical grouping and add VMs/files
- Configure Consistency Groups - Group dependent applications for crash-consistent recovery
- Set Snapshot Schedule - Define frequency based on RPO requirements
- Configure Retention - Balance storage costs with snapshot retention needs
- Add Remote Sites - Configure replication targets
- Manual Recovery - Use restore or migrate operations when needed
Protection Domain Limitations
While Protection Domains excel at basic backup and replication, they have constraints that become apparent at scale:
Manual interaction - Every VM must be individually assigned to Protection Domains, and recovery operations require manual intervention and validation.
Cluster-scoped management - Configuration is local to each PE instance, making consistent policies across multiple clusters challenging.
Limited orchestration - No automated boot sequencing, network remapping, or sophisticated failover workflows.
Basic reporting - Minimal compliance reporting and testing capabilities compared to enterprise requirements.
Static assignments - VMs remain in their assigned Protection Domains regardless of changing business requirements or application lifecycle changes.
Nutanix Disaster Recovery - Policy-Driven Evolution
Now let's explore how Nutanix Disaster Recovery transforms these concepts into a policy-driven, automation-first platform that addresses the limitations of Protection Domains while maintaining the underlying reliability.
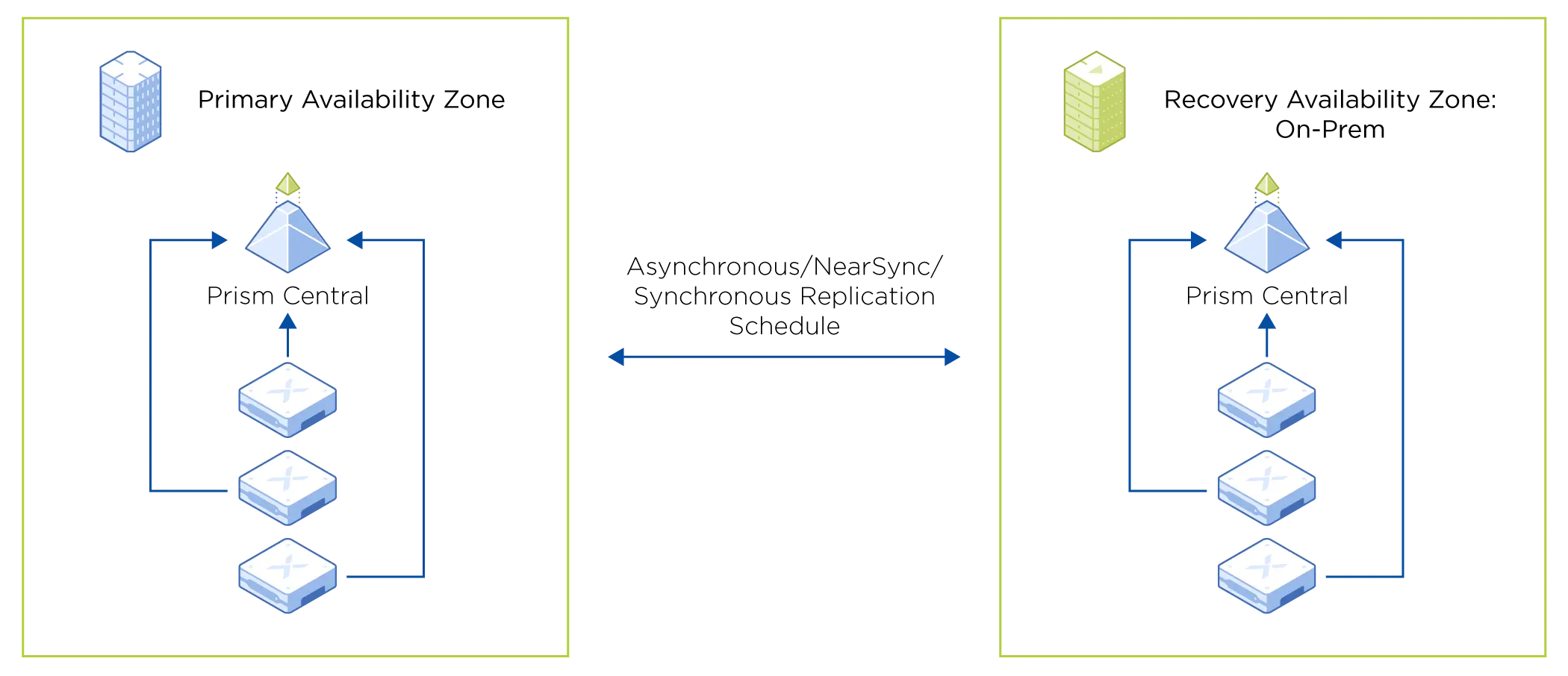
The Category Revolution
The biggest conceptual shift in Nutanix DR is moving from VM-centric to category-based management. Instead of manually selecting VMs for protection, you define categories (like "Production," "Database Tier," "Web Servers") and assign VMs to those categories. Protection policies then apply to categories automatically.
Note - You may still target individual VMs, but let's be realistic, that is not scalable!
Why categories change everything:
- Dynamic protection - New VMs automatically inherit appropriate DR policies based on their category assignments
- Consistent governance - Policies apply uniformly across all VMs in a category, eliminating configuration drift
- Simplified management - Change a policy once, and it applies to all relevant VMs immediately
- Business alignment - Categories reflect how you actually think about applications and services
Nutanix DR Constructs
Protection Policy - Defines RPO, retention, recovery locations, and target categories. This is where you set the business rules for how different application tiers should be protected. A single protection policy can apply to multiple categories and automatically include new VMs as they're created.
Recovery Plan - Your automated disaster recovery runbook that defines power-on sequencing, network mapping, and validation steps. Recovery plans eliminate the manual orchestration required with Protection Domains and provide repeatable, tested recovery procedures.
Availability Zones (AZ) - Logical representations of recovery locations, where an instance of Prism Central represents an AZ. One AZ serves as the primary AZ for protection, while one or more paired AZs serve as the recovery AZs. This means AZ relationships are established between different Prism Central instances, whether they're managing on-premises clusters or cloud environments like NC2.
Linear vs. Roll-up Retention - Sophisticated retention policies that automatically age snapshots from hourly to daily to weekly as they get older, optimizing storage utilization while maintaining granular recovery points for recent data.
The Policy-Driven Advantage
Nutanix DR implements a true policy-driven model where you define the business requirements once, and the system handles the operational complexity:
Set it and forget it - Assign categories to VMs, create protection policies for those categories, and the system automatically handles snapshot schedules, replication, and retention.
Automatic compliance - VMs inherit protection policies based on their business function, not manual configuration steps that can be missed or misconfigured.
Centralized governance - All DR policies are managed through Prism Central, providing a single pane of glass across multiple clusters and cloud environments.
Intelligent automation - Recovery plans can include custom scripts, network remapping, and sophisticated validation steps that execute automatically during failover events.
The Key Differences That Matter
Let me break down the practical differences between these approaches in terms that matter for day-to-day operations:
Management Complexity
Protection Domains - Every VM must be manually assigned. Changes require updating individual VMs or Protection Domains across each cluster.
Nutanix DR - Assign categories to VMs once. Policy changes automatically apply to all relevant VMs across all connected clusters.
Recovery Operations
Protection Domains - Manual restore/migrate operations. You need to determine what to recover, in what order, with what network configuration.
Nutanix DR - Automated recovery plans execute power-on sequences, network mapping, and validation steps with minimal manual intervention.
Scale and Governance
Protection Domains - Configuration is cluster-specific. Maintaining consistent DR policies across multiple sites requires manual coordination.
Nutanix DR - Centralized policy management with automatic propagation across availability zones. Consistent governance regardless of scale.
Testing and Compliance
Protection Domains - Testing requires manual processes and documentation. Limited built-in reporting for compliance purposes.
Nutanix DR - Non-disruptive testing with automated reporting. Built-in compliance documentation and audit trails.
Hybrid Cloud Integration
Protection Domains - Basic replication to other Nutanix clusters. Limited cloud integration capabilities.
Nutanix DR - Native integration with NC2, seamless hybrid cloud DR operations, and cloud-first automation.
Choosing the Right Approach
Both approaches have their place in the Nutanix ecosystem, and understanding when to use each one is key to building effective DR strategies.
Choose Protection Domains when:
- Your DR requirements are straightforward backup and replication
- Manual recovery processes are acceptable for your RTO requirements
- You prefer direct cluster-level management
- Budget constraints make Advanced Replication or Ultimate licensing challenging
Choose Nutanix DR when:
- You're managing multiple clusters or hybrid cloud environments
- Automated failover and sophisticated orchestration are requirements
- Compliance mandates documented, tested recovery procedures
- You need policy-driven governance across large VM populations
- Your organization demands enterprise-grade DR reporting and analytics
Advanced Capabilities - Where Nutanix DR Excels
While both approaches handle basic backup and replication effectively, the advanced capabilities of Nutanix Disaster Recovery become apparent when you need sophisticated automation, orchestration, and enterprise-grade features. Let me break down the specific capabilities that distinguish these approaches.
Automated Failover and Network Reconfiguration
One of the most significant differentiators between Protection Domains and Nutanix DR is how they handle failover operations, particularly when it comes to network reconfiguration and automated recovery orchestration.
Protection Domains require manual intervention for every aspect of failover. When you migrate or restore from a Protection Domain, you're responsible for powering on VMs in the correct sequence, updating network configurations, modifying IP addresses, and validating that applications are functioning correctly. This manual process can extend your RTO significantly and introduces the risk of human error during high-stress recovery scenarios.
Nutanix DR, by contrast, automates these complex workflows through Recovery Plans that can include sophisticated network mapping, IP address translation, custom scripting, and validation procedures that execute automatically during failover events.
Feature Comparison - Protection Domains vs Nutanix DR
| Capability | Protection Domains | Nutanix DR | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Failover | Manual restore/migrate operations | Fully automated recovery plans with one-click execution | RTO reduction from hours to minutes |
| IP Address Management | Manual reconfiguration required | Automated IP mapping and modification during failover | Eliminates network connectivity delays |
| Boot Sequencing | Manual VM power-on in correct order | Automated staging with configurable delays | Ensures application dependencies are met |
| Custom Scripts | Not supported during recovery | Pre/post-recovery scripts for advanced automation | Enables custom validation and configuration |
| Network Mapping | Manual VLAN/network changes | Automatic network translation between sites | Seamless failover to different network topologies |
| Testing Capabilities | Disruptive restore operations | Non-disruptive test failover with isolated networks | Regular testing without production impact |
| Rollback/Failback | Manual process requiring new replication setup | Automated failback with reverse replication | Simplified return to production operations |
| Compliance Reporting | Basic snapshot reports | Comprehensive test results and audit trails | Meets enterprise compliance requirements |
| Multi-VM Consistency | Consistency groups at PD level | Application-aware consistency across categories | Better application integrity during recovery |
| Hybrid Cloud Integration | Limited to Nutanix clusters | Native NC2 and cloud provider integration | True hybrid cloud DR capabilities |
Custom Scripting and Advanced Automation
The custom scripting capabilities in Nutanix DR deserve special attention because they represent a fundamental shift from reactive recovery to proactive automation. Here's what's possible:
Pre-Recovery Scripts can perform environmental preparation - updating DNS records, notifying monitoring systems, or preparing load balancers for the incoming workloads. These scripts execute before VMs are powered on, ensuring the environment is ready for the recovered services.
Post-Recovery Scripts handle application-specific configuration, database reconnection, service validation, and notification workflows. They can also integrate with external systems like ticketing platforms or communication tools to notify stakeholders about recovery status.
Validation Scripts can perform automated health checks to ensure recovered applications are functioning correctly before marking the recovery as successful. This provides confidence that your DR operation actually restored business functionality, not just VM availability.
While these automation capabilities provide powerful infrastructure-level recovery orchestration, the specific business benefits and ROI advantages of Nutanix's DR approach - including cost optimization, operational simplicity, and strategic value - will be covered in detail in a future post in this series.
Competitive Landscape - How Nutanix DR Compares
Understanding how Nutanix Disaster Recovery stacks up against other enterprise DR solutions helps contextualize its strengths and positioning in the market. Let me break down comparisons with two major competitors that represent different approaches to the DR challenge.
Nutanix DR vs Zerto
Zerto has established itself as the gold standard for near-zero RTO/RPO disaster recovery, particularly in VMware environments. However, the comparison reveals some interesting trade-offs between complexity and capability.
| Aspect | Nutanix Disaster Recovery | Zerto | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Requirements | Nutanix clusters with Prism Central | Zerto Virtual Manager appliances, separate management infrastructure | Nutanix leverages existing infrastructure |
| Replication Technology | Native AOS snapshots with Synchronous, Near-Sync, and Async options | Continuous Data Protection (CDP) with journal-based replication | Nutanix leverages existing storage; Zerto leverages existing storage |
| Hypervisor Support | AHV and vSphere on Nutanix platform | VMware, Hyper-V, AWS, Azure (multi-hypervisor) | Both support multiple hypervisors within their ecosystems |
| Cross-Hypervisor Replication | VMware to AHV and AHV to VMware bidirectional replication | Limited cross-hypervisor scenarios, primarily within same vendor stack | Nutanix enables true hypervisor migration as part of DR strategy |
| RPO Options | Synchronous (0 RPO), Near-Sync (1-15 min), Async (1+ hours) | Sub-second with CDP, configurable journal retention | Zerto achieves consistent low RPOs; Nutanix offers flexibility |
| Cloud Integration | Native NC2 integration for AWS, Azure, GCP | Cloud connectors for major public cloud providers | Nutanix offers tighter integration with its cloud platform |
| Management Complexity | Integrated into Prism Central, policy-driven automation | Separate management console, VM-centric configuration | Nutanix offers unified infrastructure management |
| Network Requirements | Leverages existing cluster networking | Requires dedicated network for replication traffic | Nutanix has simpler network architecture |
| Failover Automation | Recovery Plans with boot sequences and scripting | Virtual Protection Groups with automated orchestration | Both offer sophisticated automation |
| Testing Approach | Non-disruptive test bubbles with automatic cleanup | Non-disruptive test bubbles with isolated networks | Both support production-safe testing with similar approaches |
| Scripting Capabilities | Pre/post-recovery PowerShell and shell scripts | Pre/post-recovery custom scripts with multiple language support | Both offer comprehensive custom scripting capabilities |
| Reporting and Compliance | Built-in compliance reporting with audit trails | Built-in reporting and analytics dashboard | Both provide native reporting capabilities |
| Failback Operations | Automated reverse replication and failback workflows | Sophisticated failback with incremental re-synchronization | Both handle failback operations well |
| Learning Curve | Familiar interface for Nutanix administrators | Requires specialized Zerto expertise | Nutanix leverages existing skill sets |
| Cost Model | Included with AOS licensing, advanced features may require additional licensing | Per-VM licensing with feature-based tiers | Nutanix typically has lower total cost of ownership |
When Zerto makes sense: Multi-hypervisor environments requiring consistent replication across different platforms, extremely aggressive RPO requirements (sub-second), organizations already invested in VMware ecosystems with complex multi-vendor storage, environments needing granular replication control.
When Nutanix DR makes sense: Organizations looking to modernize from VMware to AHV as part of their DR strategy, Nutanix-centric infrastructure, preference for unified management, cost-sensitive deployments, hybrid cloud strategies centered on NC2, need for flexible replication options without additional licensing complexity.
Nutanix DR vs VMware Live Recovery (formerly SRM)
VMware Live Recovery (formerly Site Recovery Manager) represents the traditional enterprise approach to DR orchestration, focusing on comprehensive runbook automation within VMware environments.
| Aspect | Nutanix Disaster Recovery | VMware Live Recovery | Key Differences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Requirements | Nutanix clusters with Prism Central | VMware infrastructure with vCenter, Live Recovery appliances, storage replication | Live Recovery requires more complex infrastructure stack |
| Replication Technology | Native AOS with Synchronous, Near-Sync, Async options | Array-based replication or vSphere Replication | Nutanix uses native storage; Live Recovery depends on external replication |
| Hypervisor Support | AHV and vSphere on Nutanix platform | VMware vSphere only | Nutanix supports dual hypervisor approach |
| Cross-Hypervisor Replication | VMware to AHV and AHV to VMware bidirectional replication | Not supported - vSphere to vSphere only | Nutanix enables hypervisor modernization during DR implementation |
| RPO Options | Synchronous (0 RPO), Near-Sync (1-15 min), Async (1+ hours) | Depends on storage array or vSphere Replication (typically 15+ minutes) | Nutanix offers more flexible RPO options |
| Cloud Integration | Native NC2 integration for AWS, Azure, GCP | VMware Cloud integration with additional licensing | Nutanix simpler for hybrid cloud scenarios |
| Management Complexity | Integrated into Prism Central, category-based policies | Separate Live Recovery console, manual protection group management | Nutanix offers more automated policy application |
| Network Requirements | Leverages existing cluster networking | Depends on storage replication networking requirements | Varies based on storage solution |
| Failover Automation | Recovery Plans with boot sequences and scripting | Sophisticated recovery plans with extensive automation | Both offer comprehensive automation |
| Testing Approach | Isolated test networks with automatic cleanup | Test bubbles with manual network isolation configuration | Nutanix provides simpler testing workflows |
| Scripting Capabilities | Pre/post-recovery PowerShell and shell scripts | Extensive custom script integration with multiple languages | Both offer comprehensive custom scripting capabilities |
| Reporting and Compliance | Built-in compliance reporting with audit trails | Comprehensive reporting with third-party integration options | Live Recovery provides more detailed reporting capabilities |
| Failback Operations | Automated reverse replication and failback workflows | Sophisticated failback with incremental re-synchronization | Both handle failback operations well |
| Learning Curve | Familiar interface for Nutanix administrators | Requires specialized Live Recovery expertise and storage knowledge | Nutanix leverages existing skill sets |
| Cost Model | Included with AOS licensing, some advanced features require additional licensing | Significant licensing costs for Live Recovery plus storage replication | Nutanix typically more cost-effective |
When Live Recovery makes sense: Large VMware environments with complex runbook requirements, organizations with dedicated Live Recovery expertise, environments requiring extensive third-party integrations, multi-vendor storage environments that need to maintain pure VMware stack consistency.
When Nutanix DR makes sense: Organizations planning hypervisor modernization from VMware to AHV, Nutanix infrastructure investments, preference for simplified operations, cost optimization priorities, hybrid cloud strategies with NC2, environments seeking to consolidate DR and infrastructure platforms.
The Integration Advantage
What's often overlooked in these comparisons is the integration advantage that Nutanix Disaster Recovery provides. Because it's built into the same platform that's running your production workloads, you get:
Unified Management - The same administrators who manage your Nutanix clusters can handle DR operations without learning separate platforms or interfaces.
Consistent Networking - The same virtual networking, security policies, and microsegmentation that protect your production workloads automatically extend to your recovery sites.
Simplified Licensing - DR capabilities are included with AOS licensing rather than requiring separate per-VM or per-socket licensing models.
Single Vendor Support - When issues arise, you're dealing with one vendor rather than coordinating between storage, hypervisor, and DR solution providers.
Looking Ahead - What's Next in This Series
Now that you understand the fundamental differences between Protection Domains and Nutanix Disaster Recovery, we're ready to dive deeper into the practical implementation details.
In the next post, I'll dive into Protection Policies - how to design them, configure them, and align them with your business requirements. I'll cover RPO planning, retention strategies, and the category management techniques that make policy-driven DR so powerful.
Following that, I'll explore Recovery Plans in detail, including power-on sequencing strategies, network mapping best practices, and the custom scripting capabilities that enable sophisticated automation during failover events.
Final Thoughts
The evolution from Protection Domains to Nutanix Disaster Recovery represents more than just new features. It's a fundamental shift in how we approach business continuity. While Protection Domains remain a solid choice for specific use cases, the policy-driven automation and hybrid cloud capabilities of Nutanix DR are where the platform truly shines.
The key insight is that both approaches leverage the same underlying AOS replication technology, so you're getting the same reliability and efficiency regardless of which management model you choose. The decision comes down to operational requirements, scale, and the level of automation your organization needs.
Understanding these constructs is just the beginning - implementing them effectively requires careful planning and alignment with your business requirements.